
This Is The New State Of Shadow AI In 2026
Navigating the New Frontier of IT Risks… and Turning Them Into Opportunities
It starts innocently enough.
A marketing manager needs to draft ad copy by 5:00 PM but is stuck in meetings until 4:30. A developer hits a roadblock on a script and needs a quick syntax check. An HR specialist wants to summarize a dozen policy documents into a single email.
In the past, these scenarios might have led to late nights or missed deadlines. Today, they lead to a quick copy-paste into a generative AI tool. The problem is solved in seconds. It seems like productivity is soaring. The employee feels empowered.
But on the other side of the screen, corporate data — perhaps proprietary code, customer lists, or internal strategy — has just left your secure perimeter.
This is the new reality of IT. We are no longer just dealing with shadow IT in the traditional sense — where a department might swipe a credit card for a rogue SaaS license, download their preferred email client onto a work machine, or even drop some work files into a personal DropBox to get some work done after hours.
Shadow AI is faster, more pervasive, and significantly more difficult to detect than its predecessors.
Current Research Indicates a Startling Reality
81%
Reports from 2025 suggest that up to 81% of the global workforce is actively using unapproved AI tools to perform their daily tasks.
88%
Alarmingly, this trend is spearheaded by the very guardians of the enterprise — 88% of security leaders admit to using unapproved AI tools.
This pervasive adoption is exposing the cracks of the traditional “command and control” IT philosophy. The workforce has tasted the efficiency of the autonomous age, where tasks that took hours now take minutes. And they are voting with their browsers, freely accessing the tools they believe they need to succeed.
For IT leaders, this can feel like losing control. The instinct might be to lock everything down — to block the URLs, ban the tools, and retreat behind layers of policies that make it too difficult for anyone to use AI at all.
But in the era of AI, fear is a poor strategy.
Shadow AI doesn’t have to be a villain. It is much more advantageous to see it as a signal of where your business is trying to go. The most successful organizations won’t be the ones that successfully block AI. They’ll be the ones that successfully bring it out of the shadows and make it a central, secure part of their operational strategy.
Shadow IT Is Back, and It’s More Powerful Than Ever
To understand shadow AI, we have to look at its lineage.
Shadow IT has been a thorn in the side of CIOs for decades. It usually looked like a rogue Dropbox account, a Trello board set up without IT’s knowledge, or a USB full of company files. The driver was almost always friction: IT was too slow, or the sanctioned tools were too clunky.
Shadow AI shares this DNA, but it has evolved.
-
The Speed of Adoption
Traditional SaaS adoption used to require a budget, manager approval, and a lengthy setup process. But for the past decade, providers have worked tirelessly to “reduce friction.” AI-powered tools have perfected this.
Most generative AI tools have a zero-cost barrier to entry. Take ChatGPT, for example: the sign-up experience is designed to be instantaneous. With a single click using a personal Google, Apple, or Microsoft ID, a user is in. There’s no software to download, no security review to navigate, and no corporate credit card required.
By offering generous free tiers and a simple “chat” interface that feels as natural as texting a friend, these products encourage immediate use. The “deployment” time is basically non-existent. This ease of use is a win for individual productivity, but it’s exactly how AI slips past the gates of traditional IT oversight.
-
The Autonomy Factor
Previous waves of shadow IT focused on storage and workflow — employees using unauthorized platforms like Dropbox, Trello, or Asana. These tools boosted productivity, and they exacerbated existing risks: data breaches, information silos, and compliance violations due to a lack of IT visibility.
With shadow AI, the stakes have shifted.
Traditional shadow IT changed how work was done, but shadow AI actually does the work. AI agents write code, draft contracts, and analyze data autonomously. This introduces a new risk profile: when employees use unvetted AI, organizations lose control over the quality and integrity of the output. Errors in AI-generated legal documents or financial analysis can lead to significant liability and financial loss.
AI isn’t static. These tools can act and adapt. A rogue AI automating customer communications could damage a brand’s reputation, or if improperly secured, become a vector for cyberattacks.
Ultimately, the risk has evolved from where data is stored to how decisions are made. Without robust governance and oversight, AI-driven decisions can lead to rapid, escalating harm without clear lines of accountability. Establishing policies to vet and monitor these tools is no longer optional — it’s a necessity.
What Does Shadow AI Look Like in Your Organization?
So, what exactly are we dealing with? Let’s start with a definition:
-
Shadow AI refers to the unsanctioned use of artificial intelligence tools, models, or features within an organization’s environment without the explicit approval or oversight of the IT or security department.
It is dangerous not because employees are malicious, but because they are trying to be efficient in a system that hasn’t yet provided them with safe alternatives. It is pervasive because it is useful.
If you think you don’t have shadow AI in your organization, look closer. It doesn’t always look like a dedicated tab open to ChatGPT. It hides in plain sight, often embedded in tools you already trust.
Public LLMs are the most visible form of shadow AI. It usually happens when employees copy and paste sensitive company text directly into public interfaces like ChatGPT, Gemini, or Claude. Whether they are trying to summarize meeting notes, draft a quick email, or debug a complex line of code, the goal is efficiency.
The risk here is permanent. Data entered into these public models may be used to train future iterations of the tool. This means your proprietary information or sensitive IP could effectively become part of the model’s public knowledge base, accessible to anyone.
This is the insidious side of shadow AI. You might have sanctioned a project management tool like Notion or a collaborative suite like Microsoft 365. Suddenly, these platforms roll out “AI Assistant” features. An employee clicks “Summarize this document,” and data is processed by an AI sub-processor you never vetted.
For example, imagine a legal team uploading a sensitive contract to a cloud storage provider for safekeeping. The provider’s newly introduced AI feature then scans and analyzes the document to suggest possible edits or improvements. While this may seem convenient, it introduces a layer of complexity: the data is now being processed in ways that may not align with the compliance measures your original audit anticipated. Essentially, the contract isn’t just stored — it’s being actively interacted with by an AI, potentially creating gaps in your compliance strategy that weren’t previously considered.
“Write better emails!”
“Summarize YouTube videos!”
Employees often install browser extensions to boost their daily productivity and speed up repetitive tasks. However, these extensions frequently require broad read/write access to everything appearing in the browser window. This means they can see and interact with sensitive data within your internal CRM, proprietary web apps, or private administrative dashboards — often without any oversight from your IT team.
And since so many are free to use, there’s almost nothing slowing them down. This alone raises important (sometimes unanswerable) questions of who is making these, and for what purpose. When free tools are easily available and published without clear attribution, security alarms should be going off.
Developers today face immense pressure to ship code faster and more efficiently. To meet these demands, many turn to tools like GitHub Copilot or other code-generation platforms. However, if these tools are unsanctioned or used without proper precautions, they can introduce significant risks.
These platforms often analyze your proprietary codebase to generate suggestions, but this process comes with potential vulnerabilities. At best, the code suggestions are ineffective, inefficient, or just plain bad… but they get used anyway.
At worst? Your carefully crafted proprietary algorithms, designed to give your business a competitive edge, may inadvertently leave your secure repository and become part of a third-party model. This could lead to unintended exposure or misuse of your intellectual property, highlighting the need for caution when integrating such tools into your development workflow.
Identifying these forms is the first step. You cannot govern what you cannot see.
Before we explore the specific consequences of shadow AI, it’s critical to step back and consider the broader implications of unchecked artificial intelligence within your infrastructure.
While shadow AI might initially seem like a useful shortcut to achieving faster results, the lack of visibility and governance over these tools creates substantial risks that can erode system integrity, security, and performance over time. These risks are not just hypothetical — they can result in tangible fallout, impacting regulatory compliance, operational efficiency, and your organization’s overall resilience.
Said another way: if the argument for engaging in shadow AI boils down to “It’s making us faster, so what’s the harm?,” then you need to remember that speed without steering usually ends in a crash.
That’s the harm.
The Hidden Costs and Consequences of Flying Blind
Approaching this list with an understanding of how these consequences interconnect will help you appreciate the importance of proactive oversight and structured policies. Remember, mitigating these issues isn’t about resisting innovation — it’s about integrating it responsibly and making sure that your technology aligns with your strategic goals.
In early 2023, it was reported that Samsung employees had accidentally leaked confidential information to ChatGPT. In at least three separate incidents, engineers uploaded sensitive data to the public chatbot. This included source code for a new program, code related to semiconductor equipment, and even a recording of an internal meeting. They were using the tool to check for errors and summarize notes, but in doing so, that proprietary information was sent to OpenAI’s servers, potentially becoming part of the model’s training data.
This is the nightmare scenario.
When your competitive advantage lies in your intellectual property (IP), sharing it with a public model is essentially the same as broadcasting it for everyone to see. By doing so, you risk exposing the unique knowledge or strategies that set your business apart, potentially eroding the very edge that makes you competitive.
The exploding demand for AI tools has created a gold rush for cybercriminals. Employees searching for “free AI PDF summarizer” or “unblocked ChatGPT” are increasingly led to malicious browser extensions or software downloads. While traditional attacks are being made stronger by AI, novel attacks that go after the models themselves are creating a dangerous new territory most employees aren’t prepared for.
Attacks that use, or go after, AI are falling into these general categories:
- Prompt Injection: Attackers can craft inputs that manipulate the AI into revealing previous context or bypassing safety filters. A “shadow” tool without enterprise guardrails is highly susceptible to these attacks.
- Model Poisoning: Relying on unvetted open-source models introduces the risk that the model itself has been tampered with. Attackers can “poison” the weights of a model so it provides biased code suggestions or introduces subtle vulnerabilities into software builds.
- Malicious Extensions: As users install unvetted browser extensions to augment their AI experience, they inadvertently install spyware that captures all browser activity, including passwords and internal corporate URLs.
If you operate in a highly regulated industry like healthcare, finance, or legal, shadow AI isn’t just a poor practice — it’s a compliance minefield waiting to explode.
The moment an employee inputs customer PII (Personally Identifiable Information) into an unvetted AI tool, you can lose control over that data. If that tool’s servers are located in a different jurisdiction, you have likely violated strict data sovereignty laws designed to protect consumer privacy. Privacy frameworks like GDPR and CCPA are getting stronger and more authoritative every day, which puts any organization who operates beyond their local region at risk.
The risk is even more direct in healthcare. Imagine a well-intentioned employee using a free, non-compliant AI chatbot to summarize patient notes. This seemingly harmless act of seeking efficiency constitutes a direct violation of HIPAA, exposing sensitive patient data and placing the organization at risk of severe penalties.
Shadow AI poses a direct threat to an organization’s SOC 2 and ISO 27001 certification by breaking the “chain of custody” required for data compliance. Because employees use these tools without Data Processing Agreements (DPAs) or vendor security reviews, organizations cannot prove to auditors that sensitive data is being handled securely once it leaves their perimeter. The lack of audit logs for these shadow interactions makes it impossible to fulfill the monitoring and asset management controls central to both frameworks.
Shadow AI isn’t just a security risk; it’s a significant quality risk that can undermine critical business decisions.
AI models are prone to hallucinations, confidently presenting falsehoods as if they were facts. This becomes particularly dangerous when employees rely on unsanctioned tools to perform tasks like generating market research or reviewing a legal clause. If the tool hallucinates, your business could end up making decisions based on inaccurate or entirely fictional information.
Without IT oversight to evaluate the accuracy and suitability of these tools, there’s no way to know the data being used is reliable. It’s like navigating without a map — your business is effectively flying blind, increasing the risk of costly errors or poor decisions. Creating proper vetting and oversight isn’t just a best practice; it’s essential to maintaining trust and accuracy in an increasingly AI-driven world.
When every department picks its own AI tool, you end up with disconnected data silos. Marketing might rely on Jasper while Sales uses Copy.ai and Engineering leans on Copilot — yet none of these tools communicate with each other.
This lack of coordination means you often end up paying for redundant capabilities across multiple subscriptions. And it creates a significant knowledge gap. When an employee leaves the company, the valuable data, prompts, and insights stored within their personal AI account leave with them, resulting in a permanent loss of institutional knowledge.
The Opportunity: Turning Shadow into Strategy
Here is the pivot. We’ve discussed the risks, and they are real. But the knee-jerk reaction — banning AI — is a mistake.
Research indicates that 45% of employees who encounter blocking measures actively find workarounds to continue using their preferred AI tools. So if you block ChatGPT, employees will find a workaround. If you block the workaround, they will move to their personal devices where you have little jurisdiction.
Shadow IT exists because it fills a void. It tells you exactly what your employees need to succeed.
Shadow AI is a Demand Signal
The surge in shadow AI usage is the loudest signal you will ever get from your workforce. It is screaming: “We want to automate the drudgery. We want to move faster.”
Smart IT leaders view shadow AI not as a rebellion, but as a proof of concept. Your employees have already done the R&D for you. They have identified the use cases that provide the most value.
All prohibition does is create a massive “Innovation Tax.” By denying employees access to the most powerful productivity tools of the decade, the organization voluntarily puts itself at a competitive disadvantage. Competitors who figure out how to enable safe usage will outpace those who simply say “no.”
From Gatekeeper to Enabler
The goal is to shift from the “Department of No” to the “Department of How.”
Instead of:
“You cannot use ChatGPT.”
Try:
“We have procured an enterprise license for ChatGPT Enterprise/Microsoft Copilot with data protection enabled. Here is how to access it.”
By sanctioning the tools, you bring the data back inside the perimeter. You gain visibility. You gain control. But most importantly, you empower your workforce. You turn a security risk into a competitive advantage.
Companies that embrace AI strategically will outpace those that fight it. They will automate mundane tasks, free up creative energy, and innovate faster. The role of IT is to build the guardrails that allow this car to drive at 100mph safely.
A Practical Framework for Governing AI
How do you practically move from shadow to sanctioned?
It starts by shifting your (and your risk-averse colleagues’) mindset to view AI not as a threat to be neutralized, but as an identity to be managed. If AI is only perceived to be a slippery slope, the reaction to it will not foster the open communication and (most importantly) education that is required for safe use.
This concept frames AI agents (both chatbots and autonomous scripts) as non-human identities that require the same governance as human employees. In an “Intelligent IT” environment, the goal is not to stop the flow of data, but to make sure that every data flow is authenticated, authorized, and audited.
And so we must extend the concept of “Identity” beyond humans.
An AI agent running a script is a user. It needs a login. It needs permissions. It needs a lifecycle (provisioning and de-provisioning). By assigning agentic identities to AI tools, we can bring them under the umbrella of existing identity management protocols (IAM). This allows us to apply “Zero Trust” principles to AI.
Underpinning this entire framework is identity. To securely manage AI, you must know who is accessing what. A unified identity and device management platform allows you to apply conditional access policies — this makes sure only the right people, on secure devices, can access your powerful AI tools.
-
Verify Explicitly: Every AI request must be authenticated.
-
Least Privilege: AI agents should only have access to the data they absolutely need to do their job.
-
Assume Breach: Monitoring systems should assume that AI agents can be compromised and watch for anomalous behavior.
Master The 3 Faces of Identity
The world of identity management was built for human and non-human identities. But AI breaks this model. The solution to this management challenge isn’t outlawing agents: it’s updating your identity framework so you can govern them. Get this guide to discover the inherent complexities of managing AI identities—and how to evolve your infrastructure to handle them.
Get Your Copy Today
From here, we need a framework to guide our approach. We can break that down into three key pillars:
1. Discover: Turn on the Lights
You cannot manage what you cannot see. The first step is to turn on the lights.
SaaS & AI Discovery
Implement tools that scan for OAuth tokens, browser extensions, and network traffic.
Browser Management
If you manage the browser (which you should), you can see which extensions are installed and which URLs are being visited.
Risk Assessment
Categorize identified tools by risk profile. Does this tool train on our data? Does it store logs? Is it GDPR compliant?
Survey Your Users
It sounds simple, but ask them. “What tools are you using to be productive?” If you frame it as a “productivity audit” rather than a “security witch hunt,” you will get honest answers.
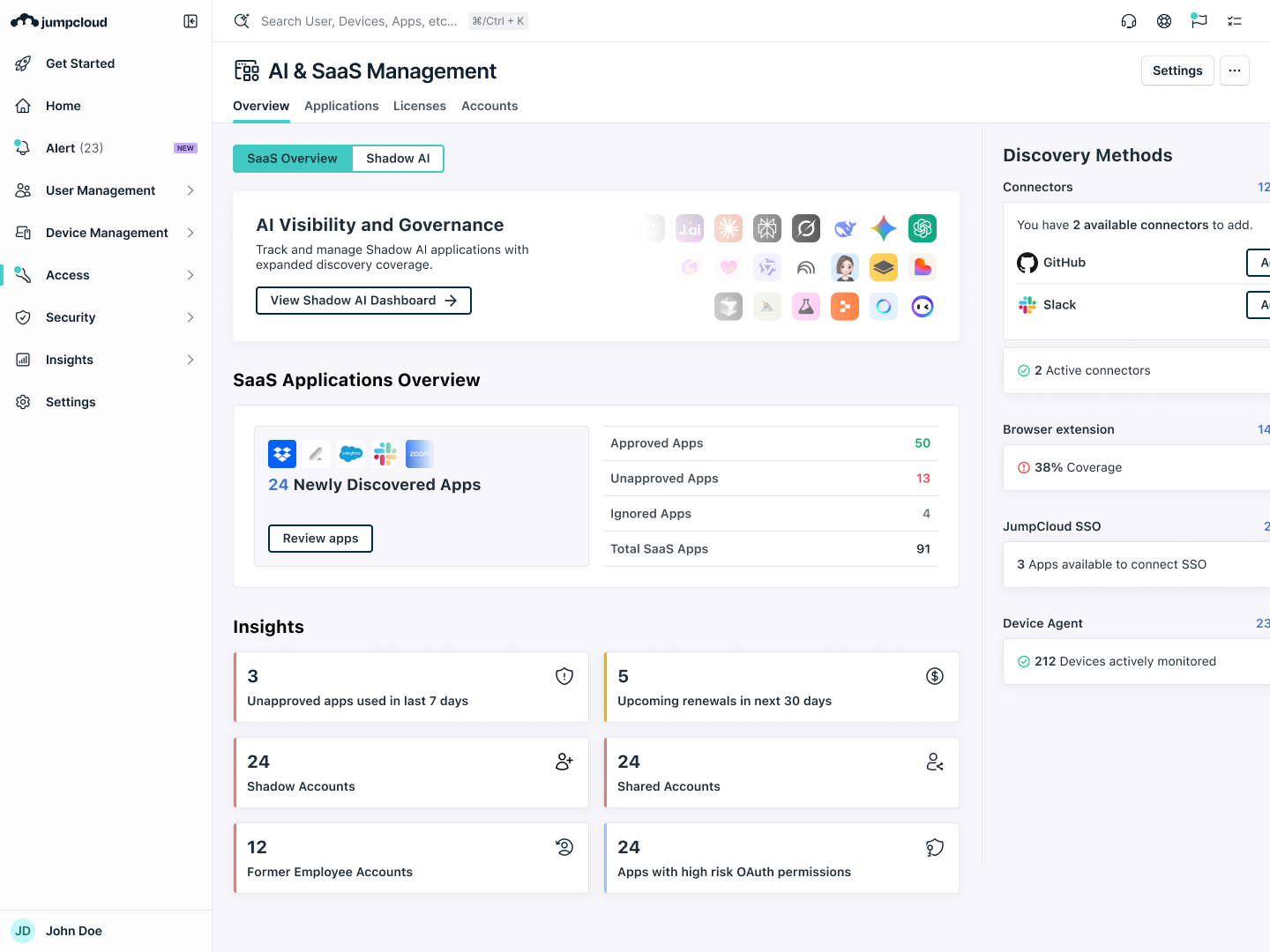
JumpCloud uncovers all AI usage across your organization, enforces identity access policies, and enables secure innovation and productivity, so you protect what matters, empower what’s next.
You can get a hands-on look at how the Shadow AI Dashboard can help you get a view of AI usage in your organization by checking out our interactive demo here.
2. Govern: Define the Rules of the Road
Governance doesn’t mean bureaucracy; it means clarity. Once visibility is established, replace bans with managed access.
Unified Identity Management
Treat AI agents as identities. Assign them permissions and access controls just as you would a new hire.
Acceptable Use Policy (AUP)
Update your AUP specifically for AI. Define what data is “Safe for Public AI,” “Safe for Enterprise AI,” and “Never for AI.”
Vet and Standardize
Select a core set of AI tools that meet your security standards (SOC2, GDPR compliance, data retention policies).
Centralize Access
Bring these tools behind your core identity provider. Use SSO to manage access. If an employee leaves, their access to the AI tool — and the corporate data inside it — is revoked instantly.

JumpCloud helps you deliver a seamless, secure work experience for your employees without interrupting their work. Fortify your defenses with precise SaaS access controls, ensuring compliance and safeguarding your organization’s security standards.
You can get a hands-on look at how to use SaaS access controls to set how your users can access certain SaaS apps. by checking out our interactive demo here.
3. Enable: Build the “Yes” Environment
This is the most critical step. The ultimate goal is to turn AI from a risk into a competitive advantage.
Create an AI Toolkit
Publish a list of approved, vetted tools for common use cases (coding, writing, image generation).
Training
Don’t just give them the tool; teach them how to use it securely. Teach them about prompt engineering and how to spot hallucinations.
Sandbox Environments
Give developers and power users a safe, isolated environment to experiment with new AI agents without risking production data.
The Trust Loop
By providing secure, effective tools, IT rebuilds trust. Employees will voluntarily migrate from shadow tools to sanctioned tools if the sanctioned tools are effective and safe.

Discover how fintech leader Refyne rebuilt its IT foundation from the inside out to support rapid global expansion and engineer organizational trust. By unifying identity and device management with JumpCloud, they achieved 90% faster onboarding and slashed IT resolution times by 80%.
We weren’t just deploying software. We were redesigning how trust operates inside the company…who gets access to what, when, and how.
– Vineet Mishra, Head of Information Security, Privacy, & IT, Refyne
Bring Shadow AI into the Light and Build Your Future with Confidence
The resurgence of shadow IT in the form of AI is a wake-up call. It is a reminder that technology moves faster than policy. But it is also an invitation.
We are standing on the precipice of the biggest shift in work since the internet. You have a choice. You can spend your energy playing whack-a-mole, trying to suppress the tools that your employees are desperate to use. Or, you can take the wheel.
By bringing AI out of the shadows, you do more than just secure your data. You build a culture of trust. You signal to your organization that IT is a partner in innovation, not a barrier to it.
The future belongs to the organizations that can run fast and stay secure.
It starts with visibility, it is sustained by governance, and it flourishes with enablement. That balance is possible.
You got this.
Ready to bring your IT environment out of the shadows?
The transition from a “Shadow AI” victim to proactive leader requires the right partners and the right platform. The future of identity, security, and device management is unified, open, and intelligent.
To explore the practical implementation of these strategies, access deeper technical deep dives into Agentic AI, and connect with industry leaders shaping the future of the autonomous workforce, we invite you to join us at JumpCloudLand. JumpCloudLand is our annual free, virtual conference built for the IT leaders actively shaping the IT future. If you’re guiding your organization through the complexities of IT modernization, secure AI adoption, and building a future-proof security strategy, this event’s for you.
February 10, 2026
Unlock the strategic insights you need to enter the latest era of IT with confidence. Learn from global experts, access dozens of tailored sessions, and connect with peer IT decision-makers. These sessions won't tell you which path you take. But they will provide the map, the gear, and the expert guidance to help you and your team forge a flexible, modern IT future.
Discover the future of IT. Register today.
