VaultOne enhances control and security over database access by letting you configure blocking rules directly within the platform. These rules can restrict specific commands, block SQL patterns, and even modify user-executed queries.
- Log in to VaultOne platform.
- Go to Databases > Blocking Rules and click Create.
- In the General tab, enter the relevant details:
- Name: A descriptive name for the rule.
- Priority: The execution order for the rule. The lower numbers have higher priority.
- Severity Alert: Choose the required alert level. If a user triggers a blocked command, an alert will be generated for administrators and, if configured, sent to your Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) system.
- Notes: Any additional information.
- In the Rule tab, configure the following blocking options:
- Command Blocking: Block specific commands by listing them under this option.
- SQL Pattern Blocking: Block SQL query patterns using standard SQL scripts or regular expressions (regex).
- Replace Query: Modify queries to restrict certain information. For example, to prevent the password column from being shown when a user runs SELECT * FROM users, you can set a replacement query to SELECT id, name FROM users. This ensures that only the id and name columns are returned, enhancing data security.
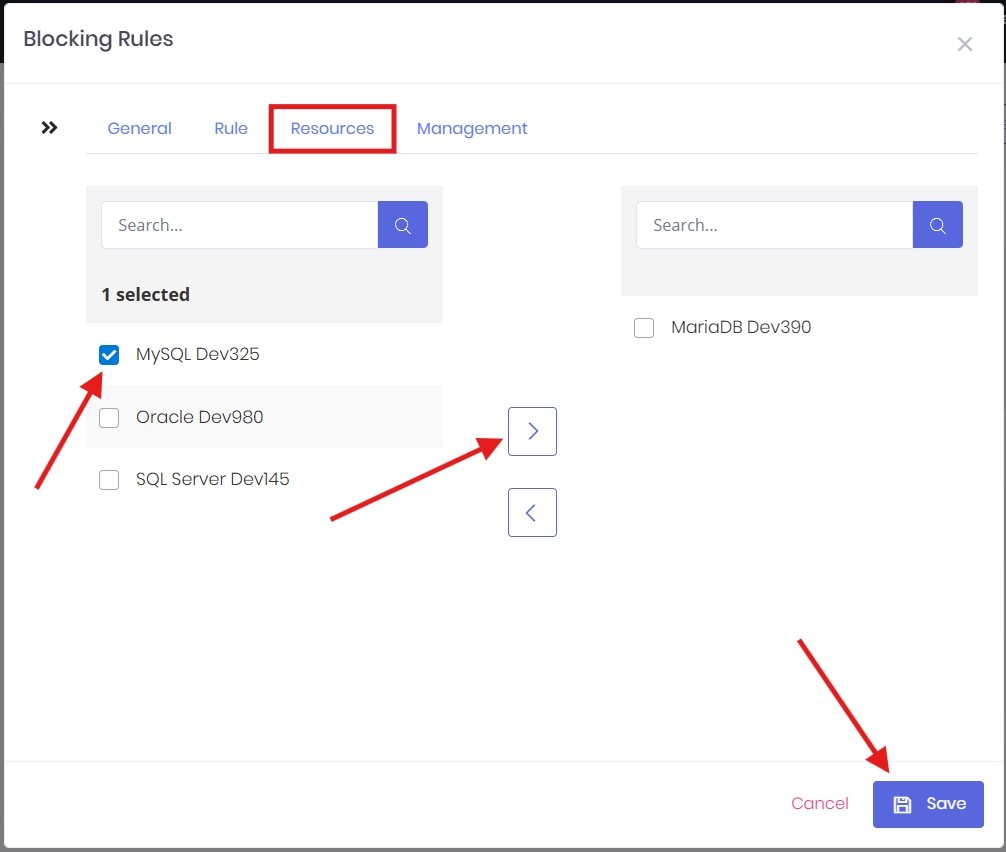
- In the Resources tab, select which resources the rule will apply to. The left-hand list shows all available resources to apply a rule. From this list, select the resources you want and use the right arrow to move them to right to the assigned list.
- In the Management tab, click Add User or Add Groups, to select users or groups to be exempted from the restrictions defined by the rule.
- Click Save to apply the rule.
You can also create blocking rules while adding a new database:
- Log in to the VaultOne portal.
- Go to Databases > Add Database.
- Go to Blocking Rules tab and click New.
- In the General tab, enter the relevant details:
- Name: A descriptive name for the rule.
- Priority: The execution order for the rule (lower numbers have higher priority).
- Severity Alert: Choose the required alert level. If a user triggers a blocked command, an alert will be generated for administrators and, if configured, sent to your Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) system.
- Notes: Any additional information.
- In the Rule tab, configure the following blocking options:
- Command Blocking: Block specific commands by listing them under this option.
- SQL Pattern Blocking: Block SQL query patterns using standard SQL scripts or regular expressions (regex).
- Replace Query: Modify queries to restrict certain information. For example, to prevent the
passwordcolumn from being shown when a user runsSELECT * FROM users, you can set a replacement query toSELECT id, name FROM users. This ensures that only theidandnamecolumns are returned, enhancing data security.
- In the Exceptions tab, click Add User or Add Groups, to select users or groups to be exempted from the restrictions defined by the rule.
- Click Save.
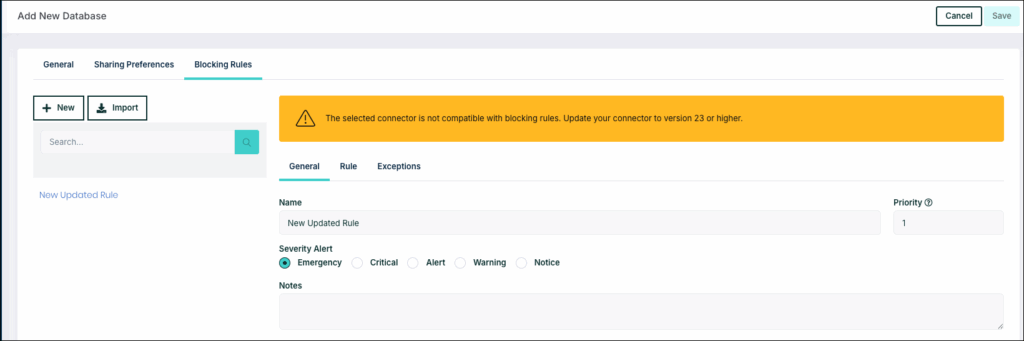
Important: Exceptions configured in this way apply only to the specific database.
Back to Top