How many times do you reach for your mobile device every day?
The average American checks their smartphone once every 4 minutes. Psst: that’s more than 125,000 times per year. Statistics for daily tablet and laptop usage are also impressive.
Our collective compulsion to stay digitally connected combined with the rise of remote work has significantly impacted how we get stuff done. Record numbers of employees are logging into Zoom meetings while running errands, making lunches, and brushing teeth.
This means more people are working across more devices, and that presents a real challenge to IT admins who need to manage activity.
Unfortunately, convenient network access has also come at the price of mobile data breaches. The good news is mobile device management (MDM) solutions are capable of thwarting most attacks and providing the necessary tools to effectively manage and support different types of devices no matter where they reside.
This article will take a deeper look at the importance of MDM, how it works, and why some organizations struggle to prioritize it. We’ll also discuss the benefits of prioritizing mobile cybersecurity before comparing the best MDM management solutions.
The Current State of Mobile Device Management

As reported in Verizon’s Mobile Security Index 2022, 45% of respondents said their organization had experienced a mobile device security incident that led to data loss, downtime or other negative outcomes. Furthermore, 73% described the impact of the attack as major.
The worst part? Many of the incidents could have been avoided by following mobile device management best practices. As Verizon mentions:
Mobile devices are prone to many of the same attacks as other devices. Most phishing attacks and badly coded sites can affect them; mobile users might even be more vulnerable. And there are also mobile-specific exploits—like malicious apps and rogue wireless hotspots.
We’ll begin by answering the most common question:
What Is Mobile Device Management?
Mobile device management (MDM) refers to the practice of enrolling, configuring, and securing portable devices in the workplace. Though some vendors use the term to solely describe smartphones, it’s worth emphasizing that MDM also includes tablets and laptops.
IT managers use MDM software to customize mobile device settings, enforce user policies, and enhance cybersecurity. So, MDM is both a software solution and an IT management practice.
Common MDM tasks:
- Install applications
- Set network preferences
- Activate user accounts
- Determine permissions
- Decommission devices
When selecting an MDM solution, IT managers and managed service providers (MSPs) have many choices. Different types of MDMs support different types of devices, capabilities, and operating systems. Regardless, all MDM platforms fall into two distinct categories: on-premise and cloud-based MDM.
Benefits of Mobile Device Management
One of the biggest motivators of implementing mobile device management is reduced security breach instances. But most organizations gain several additional benefits from implementing effective MDM programs. Here’s a quick look at the security-focused perks that come with MDM:
- Reduced costs: Less likely to encounter costly breaches.
- Bird’s-eye security: Enables remote oversight of users, devices, and applications to scan for threats remotely.
- Increased peace of mind: Data backup to prevent loss of crucial data.
- Improved housekeeping: Offers automatic deletion of temporary storage queues to free up space and reduce clogging.
- Controlled updates: Admins dictate when updates are installed on devices.
- Encrypted communication: Supports the secure communication of proprietary information between employees.
- Increased efficiency: Improves onboarding experience for new hires.
- Enhanced convenience: Safeguards bring-your-own-device (BYOD) policies.
With benefits like these it’s no surprise that analysts expect the demand for MDM solutions to grow. Experts predict the $4.5 billion global MDM market to grow 24% by 2028.
How Does Mobile Device Management Software Work?
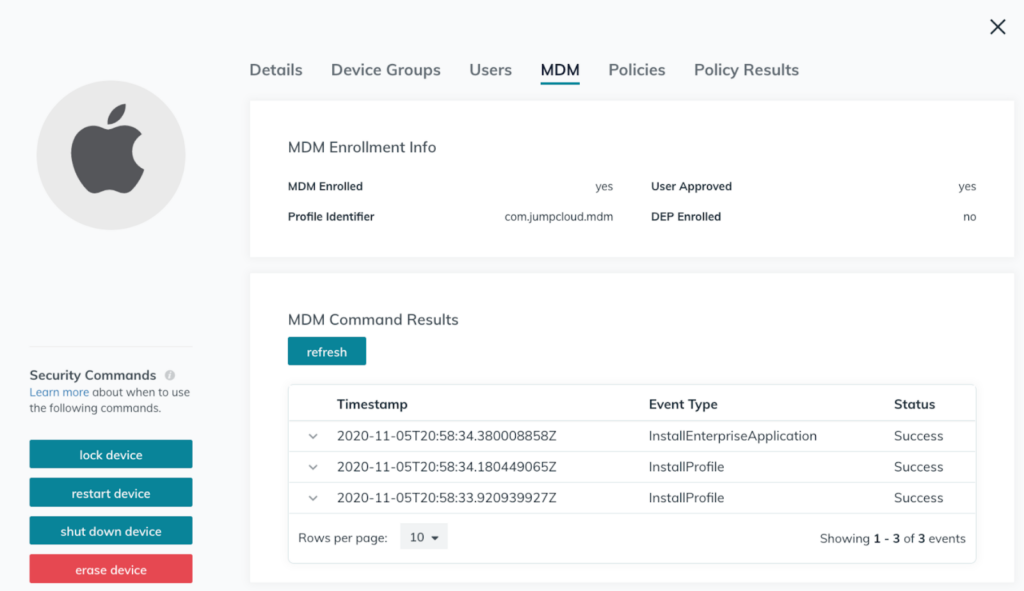
The initial setup of mobile device management software varies from platform to platform. But, for most MDMs, the process begins with enrolling devices in the software or server. Depending on the particular MDM solution, enrollment may happen through registering devices with vendor-specific programs (e.g., Apple, Google, Samsung, and Microsoft) or by adding devices manually via tokens, QR codes, NFC chips, or email/SMS.

Once devices are enrolled, admins simply login to their MDM portals for a bird’s-eye view of what’s happening. IT admins then use their management consoles to push configurations and applications to enrolled devices over the air (OTA).
Technically speaking, the MDM server (software) sends out a set of commands that are applied to devices through application programming interfaces (APIs) built in the operating system.
Cost of Mobile Device Management
According to a 2021JumpCloud survey, 47% of small and mid-size enterprises (SMEs) plan to spend more on mobile technologies, while 58% plan to spend more on remote management. Do you fall into this category?
Today’s IT managers face the immense responsibility of reducing departmental spending in the face of inflation, supply chain issues, and competing budgetary requests. Managers must optimize their operations while keeping their budgets lean.
The good news? User-based pricing is now available for budgets of all sizes. Admins can also take advantage of free trial versions to test out MDM systems before making a commitment.

The JumpCloud Directory platform is ideal for organizations wanting to consolidate identity and access management (IAM) with MDM — without breaking the bank.
Our platform features macOS and Windows MDM capabilities as a native functionality of its general device management capabilities. Admins can also enjoy group policy functions, ad hoc command execution, and a convenient single sign-on (SSO) mechanism that isn’t available anywhere else.
Of course, deploying any new type of technology isn’t without its challenges. Let’s take a closer look at common roadblocks IT teams should be aware of before upleveling MDM systems.
Challenges of Mobile Device Management
To get the most out of any managed mobility solution, admins must understand the costs, use cases, and challenges upfront. Obviously, failing to effectively manage remote work devices poses security risks, but what does that actually mean?
Below are the most common challenges of mobile device management:
1. Network Access Control
Digital workspaces are fielding requests from employees wanting to use both company-issued and personal mobile devices. This hybrid approach makes it difficult to regulate network access without jeopardizing security.
It’s crucial to ensure employees have constant access to company systems, apps, and data they need to work while keeping everything safe and secure. After all, it’s not a business unless people are getting work done! But balancing practicality with security is an ongoing challenge for most IT managers.
Fortunately, network access control (NAC) tools, like those found in the JumpCloud Directory, allow admins to enforce security policies that both users and devices must comply with to receive access.
2. Data Security
Another headache associated with personal mobile devices in virtual work environments? The more devices connected to a network, the more entry points cybercriminals have to infiltrate company systems.
Unfortunately, smartphones and tablets pose heightened security risks because they often contain less comprehensive anti-malware software compared to laptops and desktops. On the other hand, laptops and desktops are still the primary vehicle through which work gets done, and thus continue to be a primary target for enterprising criminal organizations despite gains being made in endpoint security. Again, robust MDM solutions can help businesses plug vulnerable data gaps and secure their mobile environments across all device types.
They accomplish this goal by separating personal and corporate profiles on personal mobile devices, automating data encryption, and engaging “lock and erase” functionalities that help ensure company data doesn’t get into the wrong hands should devices become lost or stolen.

3. User Experience
Of course, admins must also consider user experience when managing mobility. MDMs that severely limit certain device functionalities can frustrate employees.
For example, overly vigilant settings could flag frequently used software as “vulnerable,” that workers rely on to accomplish daily tasks. This could motivate workers who rely on said software to complete daily tasks to jailbreak devices.
With that said, it’s essential to consider how employees feel before choosing an MDM solution and whether it will impact their productivity and performance.
4. Migration
At some point, an organization might need to replace its MDM software. Whether the change is motivated by cutting costs or wanting an upgrade, software migration can be challenging — to say the least.
It’s not unusual for admins to underestimate the amount of time it takes to locate, migrate, and organize data into a new system. Besides exercising caution not to lose or corrupt data, organizations must consider the resources required to change course.
Our IT experts recommend preparing for the migration months in advance. Develop a clearly written plan, make a task force, and communicate essential details to ensure everyone understands their responsibilities moving forward.
5. BYOD Policies
The number of personal devices used for work has only increased with the adoption of digital workspaces. Needless to say, supporting all these devices has become a major challenge. There’s frequent onboarding and offboarding as remote employees acquire new devices and discard old ones. Additionally, it’s almost impossible to keep up with the entrance of new mobile devices with new technologies in the marketplace!
Unfortunately, few organizations have effective BYOD policies in place. Why? Many admins assume MDM software automatically takes care of BYOD before investing in a platform, while this is not the case.
6. Lack of Skilled Workers
According to the World Economic Forum, only 27% of small companies and 29% of large companies have the digital talent necessary to fill available roles.
The problem is not lack of technology but lack of talent. With that said, one of the biggest hurdles companies face in the deployment of MDM solutions is a short-staffed IT department to get the job done.
Of course, all of these challenges can be overcome with the right strategies, policies, and MDM software at your disposal. Let’s dive into how to get started with MDM.
Best Practices for Virtual Device Management
Follow these mobile device management best practices for smooth deployment:
1. Identify Your MDM Needs
Before you even begin thinking of investing in an MDM solution, identify your needs and understand the types of devices you’ll be managing. Some questions to ask during the initial assessment include:
- What types of devices will we be managing (laptops, tablets, smartphones)?
- What are their primary operating systems (Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, and/or iOS/iPadOS)?
- How many devices are in our environment?
- What tasks will workers use the devices to complete?
- Which applications will they need for specific tasks?
- How are devices currently connected to the network?
- What areas do we absolutely need to improve upon?
Only when you’ve answered these questions, you’re ready to plan your MDM implementation.
2. Automate to Save Time
It’s no secret that automation saves time, but it also simplifies MDM usage and minimizes security risks. Choose software with advanced reporting functionality that immediately alerts admins of policy violations.
Such violations should trigger automatic device locking, selective data wiping, or the appropriate actions depending on the level of control breach. Automated reports also make it easy to retrieve and analyze data for informed decision-making.

3. Enforce Strong Password/MFA Policies
In addition, enforce strict password and multi-factor authentication (MFA) policies. It’s the first step to securing mobile devices and sensitive company data by ensuring only authorized personnel can access them.
Some basic password policy guidelines worth considering include:
- Enforce complex passwords wherever possible
- Prohibit password sharing and reuse
- Set minimum and maximum password ages
- Require the use of password managers to help ensure password complexity and diversity needs are met
Beefing up your organization’s password policies is by far the simplest way to strengthen mobile security from wherever you are right now.
4. Backup Files and Data
Ten percent of organizations don’t back up their data at all, while 50% of professional users believe backups aren’t necessary. This is an extremely troubling statistic considering that 68% of users lose data due to accidental deletion, hardware failure, software failure, or out-of-date backups!
Mitigate the risk of data loss by creating standard operating procedures to automatically back up files and data. Modern MDM solutions like JumpCloud run on cloud-based storage that coincides with automated backups. Translation: there is no need to rely on local drives anymore.
5. Whitelist, Blacklist, and Update Applications
Another essential aspect of MDM is keeping software updated. Regular software updates strengthen IT environments, reduce system vulnerabilities, and make it difficult for cybercriminals to infiltrate networks.
Consider restricting rooted devices and only allowing approved apps for company use to enhance network security. In addition, blacklist any relevant unauthorized apps.
6. Keep Systems Updated
Up-to-date applications are only as effective as their operating systems. So, don’t forget to keep your OS up to date too. Outdated systems can also slow down software functionality, making for unpleasant user experiences. And cumbersome UX leads to unproductive downtime!
7. Gather Support
In most instances, setting up an MDM system is fairly straightforward. But that doesn’t mean you won’t encounter unforeseen challenges down the line. Ensure your IT department has access to support services before settling for a particular vendor.
In addition, make sure the platform comes with support for any pain points in the MDM process — both before and after installation.
A reliable MDM vendor will have resellers, managed service providers (MSPs), carriers, and other strategic partners you can work with hand in hand to get the best out of your platform. They will supplement the efforts of your IT team.
8. Regular Safety Training for Employees
Every MDM solution is built differently. So, before installation, ensure all relevant users understand your platform’s features and how they work. You can even organize for the vendor to run a training session for employees.
After installation, regularly remind team members of security policies, best practices, and safe use of the MDM. Include mobile device management policies in new employee orientation training and company manuals. And evolve your training as your technology and security advancements change.
Finally, review MDM policies and retrain employees on updates routinely.
MDM Solution Comparisons
This may sound like an over-simplification, but choosing any software solution is a lot like buying toothpaste. Grocery shoppers often experience overwhelm when navigating the toothpaste aisle. Author and psychologist Barry Schwartz calls it the “paradox of choice.”
When greeted by a variety of brands — all claiming to do more or less the same thing — shoppers often become paralyzed with indecision. Alternatively, fast-growing startups are known to prematurely select software platforms without considering their comprehensive needs.

Each vendor claims to have specific capabilities for specific wants, needs, and concerns. The unique tooth care goals/preferences will, ultimately, dictate final purchase decisions.
Similarly, some MDM tools cover only basic security features, while others include extra layers of protection. Here’s a list of features you’ll likely to come across:
- Security requirements for passwords
- Basic settings (e.g., locking screens)
- App restrictions and permissions
- Location tracking
- Remote locking and wiping
- Forced updates
- Data encryption
Unfortunately, MDM solutions are rarely system-agnostic. The diverse needs within one organization often dictate using several MDM tools, matching each operating system/device with its own tool. If you have a heterogeneous OS environment, shortlisting solutions that support this can pay dividends down the road, even if the specific feature set or upfront costs are less attractive.
Factors to consider when weighing options include the challenges you’re looking to solve, the types of devices and OSs you need to manage, and whether you want a comprehensive device management solution versus a point device solution. Below are the primary different categories of MDM solutions:
Windows MDM
A Windows MDM solution can help simplify the management of Windows devices by securing, monitoring, and auditing them. Admins can easily enroll devices, assign users, distribute apps and content, and enforce data security policies with Windows MDMs. For those overseeing Windows-only environments, Microsoft Intune is worth considering.
Apple MDM

Apple devices were rarely used outside of education or creative sectors until the 2010s. As such, admins didn’t give much thought to Mac device management. The security risks posed by a handful of employee-owned devices seemed minimal. However, this is no longer the case. Apple products now far outnumber Windows devices in many modern organizations.
In recent years, Apple has released several security enhancements to improve both user privacy and organizational transparency. But it’s recommended that admins use official Apple MDM vendors to further safeguard data located both on prem and in the cloud.
We recommend Jamf for those seeking basic mac device management capabilities. For those looking to combine MDM with identity and access management (IAM) in a heterogeneous environment, we recommend the JumpCloud Directory.
JumpCloud is an Apple-certified MDM vendor that provides deployment for macOS workstations through the platform’s Apple Device Enrollment Plan (DEP).
Linux MDM

Even though Linux OS only accounts for 2.2% of the global OS market, IT admins must still consider it as a core part of their device fleet. Managing Linux devices is a big challenge for many organizations today.
Ensure every system and server is patched, processes are functioning as intended, log files are rotated, and the right users are on each device among others. This makes Linux virtual device management a task only a few IT admins want to undertake. But the right Linux MDM tool can make device management possible for most administrators.
Open Source MDM
Several high-quality open source MDM solutions are now available. Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) without expansive budgets often go for open source MDMs. The open source platforms are free and provide a variety of customization options. With that said, open source often necessitates a greater time investment in terms of initial setup.
Until recently, MDM software solutions for each of the aforementioned categories were only available in on-premise formats that made it difficult to oversee both on-prem and off-prem devices. But the growing shift toward remote work is now demanding MDM solution compatibility with heterogeneous environments, which brings us to where we are now.
With a name like JumpCloud, you won’t be surprised to hear our endorsement of cloud platforms. Cloud software provides an extraordinary reduction in cost and time compared to its traditional counterparts. Alternatively, on-prem servers necesitate heavy lifting, longer timeframes, and higher costs from IT teams.
Despite recent leaps made across the marketplace, most virtual device management solutions still don’t allow comprehensive device management. You’ll have to enlist the help of JumpCloud for that.
The Evolution of Mobile Device Management

Several important events happened in 2001: Nickelback released the worst one-hit-wonder known to mankind. Apple released a revolutionary service called iTunes.
And SOTI became the first real mobile management solution to gain traction amongst tech-heads. But MDM didn’t really take off until mobile devices had officially gone mainstream around 2010. Throughout the decade, mobile device management capabilities steadily improved.
Organizations could manage entire device lifecycles, including asset management, configuration management, and remote wipes. However, despite the small usage percentage of Apple and Linux devices, the marketplace exclusively catered to Microsoft OS for a while.
It didn’t take long for Microsoft Windows Active Directory to become the de facto, premise-based platform for managing group policies, controlling user accounts, and providing centralized data management.
Over the decade, MDM solutions evolved to support features like:
- Containerization: As organizations adopt BYOD programs, MDMs are expanding to allow clear separation of personal and company assets on a single device. This ensures that IT admins don’t infringe on the privacy of employees while corporate assets (apps and data) can’t be accessed without proper authentication and used for personal gain.
- Mobile application management (MAM) and mobile content management (MCM): Modern MDM solutions also offer MAM to help organizations manage and control the purchase, management, distribution, and deployment of bulk apps. MCM, on the other hand, facilitates seamless and secure sharing of enterprise content and data across managed devices.
- Remote control and data wipe: In the event of loss or theft, IT admins can easily wipe sensitive company data before thieves download it. This helps companies maintain the integrity of their assets.
Emerging trends influencing MDM development include security challenges with internet of things (IoT) devices, deep packet inspection to tackle malicious traffic, and devices with varied configurations. Expect MDM solutions to become more relevant, agile, and stronger.
The Evolution of MDM in Heterogeneous Environments
It’s worth emphasizing that developers originally created MDM in segregated environments. Google made MDMs for Android systems, Apple developed solutions for iOS and macOS, and Microsoft did so for its Windows operating systems.
Of course, working in a Windows-centric workspace is no longer a given. Organizations are now switching to cloud-based applications, remote work policies, and BYOD at an astounding rate. For this reason, cloud-based MDM has emerged as the superior solution for heterogenous and remote work environments.
JumpCloud Directory’s architecture streamlines MDM by allowing IT admins to make fleet-wide configurations to multiple types of devices and operating systems from a single console. Even better, with JumpCloud for Google Workspace, IT teams can now unify identity and access management for added convenience and security.
Consolidate MDM with JumpCloud Directory Platform
JumpCloud’s iOS and Android mobile device management empowers IT admins to manage COD and BYOD mobile device management policies without stress. Additionally, the cloud-based platform combines its user-friendly MDM solution with IAM, MFA, and SSO capabilities.
Translation: Securing mobile device usage within a Zero Trust security framework just got a lot easier. Click here to learn more about device management with JumpCloud.






